Loan refinancing is a powerful financial tool that allows borrowers to replace an existing loan with a new one, often with improved terms. Whether for mortgages, auto loans, student loans, or business debt, refinancing can significantly impact your financial health. However, like any financial decision, it comes with both benefits and drawbacks.
In this detailed article, we explore the pros and cons of loan refinancing, helping you make an informed choice tailored to your financial goals.
What Is Loan Refinancing?
Loan refinancing involves paying off an existing loan by taking out a new loan, usually with better terms such as a lower interest rate, reduced monthly payments, or altered loan duration. The goal is often to save money, improve cash flow, or adjust the loan to better fit current circumstances.
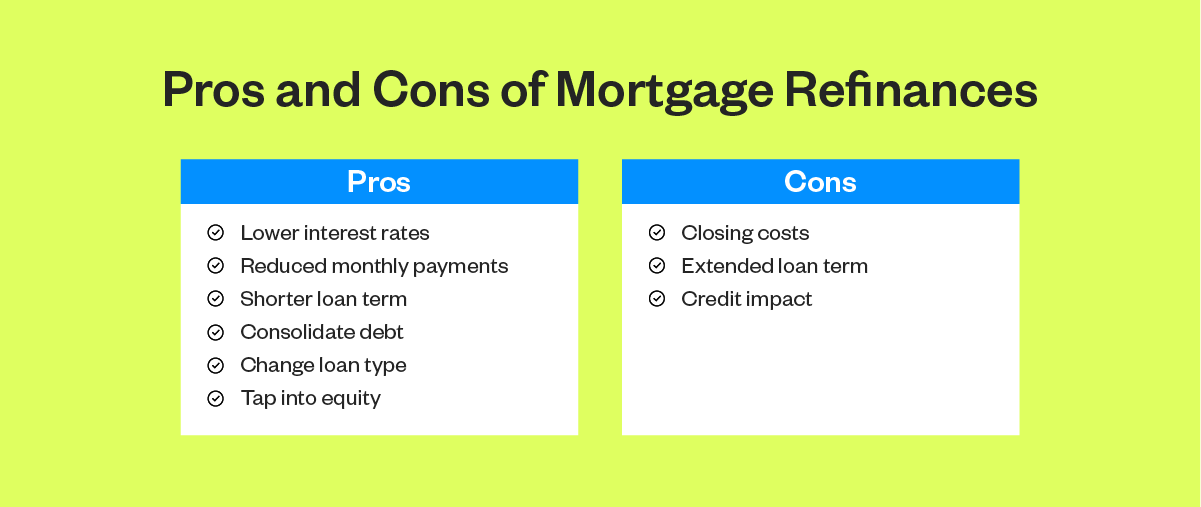
Pros of Loan Refinancing
1. Lower Interest Rates
One of the most common reasons to refinance is to secure a lower interest rate. A reduced rate can:
- Lower monthly payments
- Decrease total interest paid over the life of the loan
- Improve overall financial flexibility
2. Reduced Monthly Payments
Refinancing can extend the loan term, resulting in lower monthly payments and easing cash flow. This is particularly helpful for borrowers facing financial strain.
3. Debt Consolidation
Refinancing can combine multiple loans into a single payment, simplifying finances and potentially lowering interest rates on high-cost debt.
4. Change Loan Terms
Borrowers can shorten or lengthen loan terms. Shortening can save interest costs and build equity faster, while lengthening can reduce monthly payments.
5. Switch Loan Types
Refinancing allows switching from an adjustable-rate to a fixed-rate loan, providing payment stability and protection from interest rate hikes.
6. Improve Credit Score
By refinancing to better terms and making consistent payments, borrowers may improve their credit profiles over time.
Cons of Loan Refinancing
1. Upfront Costs and Fees
Refinancing typically involves fees such as application, origination, appraisal, and closing costs. These expenses can offset savings, especially if you plan to keep the loan for a short period.
2. Longer Loan Term Can Increase Total Interest
Extending the loan term to reduce monthly payments may result in paying more interest over time, increasing the overall cost of the loan.
3. Risk of Losing Benefits
Some loans, like federal student loans or mortgages, may have borrower protections, forgiveness programs, or tax benefits that could be lost upon refinancing.
4. Qualification Requirements
Borrowers must meet lender criteria, including credit score, income, and debt-to-income ratio. Poor credit or financial instability may limit refinancing options or increase costs.
5. Potential for More Debt
Lower monthly payments might encourage some borrowers to take on additional debt, leading to financial strain.
When Does Refinancing Make Sense?
- When current interest rates are significantly lower than your existing loan
- If your credit score has improved since taking out the original loan
- To reduce monthly payments during financial hardship
- To switch from variable to fixed-rate loans for predictability
- To consolidate high-interest debts into a lower-rate loan
When to Avoid Refinancing
- If you plan to sell or pay off the loan soon
- When upfront fees outweigh potential savings
- If refinancing causes loss of valuable loan benefits
- When your credit profile has declined, increasing refinancing costs
Tips for Successful Loan Refinancing
- Calculate the break-even point: Compare the costs of refinancing with potential monthly savings to determine how long it will take to recoup expenses.
- Shop around: Get quotes from multiple lenders to secure the best terms.
- Understand all fees: Request a detailed breakdown of closing costs and fees.
- Review loan terms carefully: Ensure you understand interest rates, payment schedules, and penalties.
- Consider timing: Market rates and your financial situation should align for maximum benefit.
Final Thoughts
Loan refinancing offers significant advantages, such as reducing interest rates, lowering monthly payments, and improving loan terms. However, it is not without risks, including fees, potential loss of benefits, and extended debt periods.
Careful evaluation of your financial goals, loan details, and market conditions is essential before refinancing. When done thoughtfully, refinancing can be a strategic step towards financial stability and savings.